I assume you’re referring to “dialysis.” Dialysis is a medical treatment that is used when a person’s kidneys are no longer functioning adequately to remove waste and excess fluid from the blood. It is a life-saving procedure for individuals with kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or chronic kidney disease stage 5 (CKD-5).
Dialysis is a critical treatment for people with kidney failure because it helps to maintain the balance of electrolytes, remove toxins, and manage fluid levels in the body. However, it is not a cure for kidney failure, and patients typically require ongoing dialysis treatment or a kidney transplant to survive.
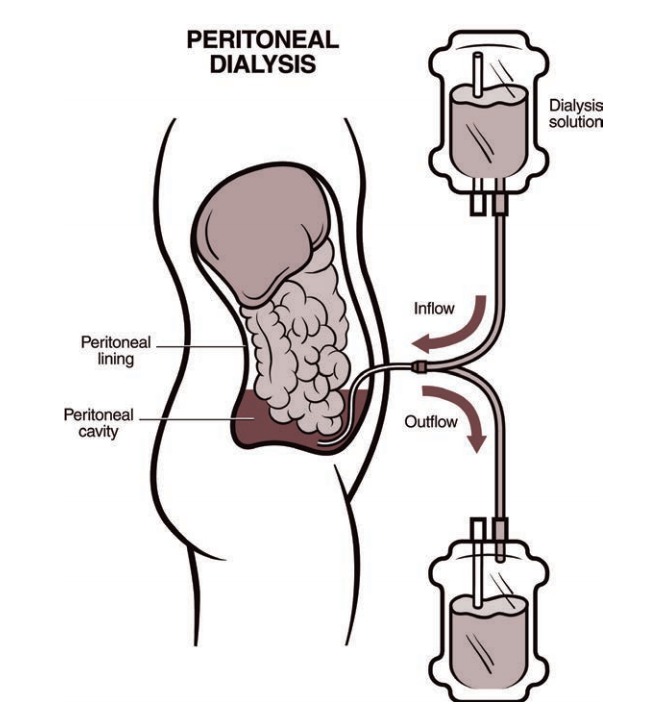
In addition to the two primary types of dialysis, there are variations and different modalities of treatment available, such as continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) within peritoneal dialysis, as well as home hemodialysis options.
Patients undergoing dialysis treatment often work closely with a healthcare team, including nephrologists and dialysis nurses, to manage their condition and maintain their overall health. The choice of dialysis modality depends on a patient’s medical condition, lifestyle, and preferences, and it is made in consultation with their healthcare providers.